A Comprehensive Guide to Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) and Career Opportunities
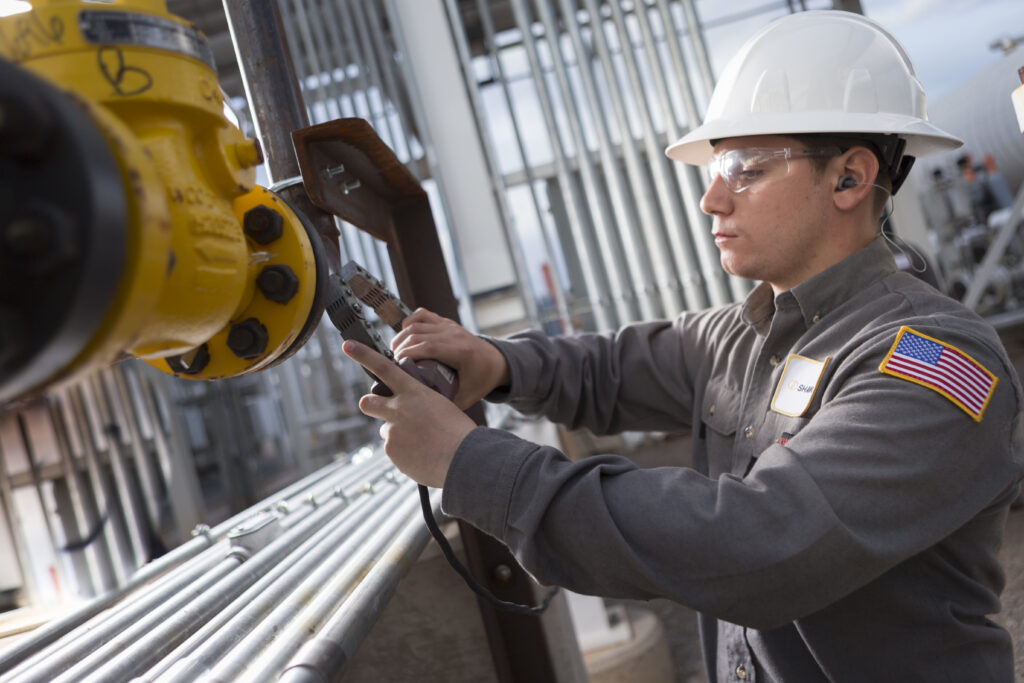

Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) refers to a collection of techniques and processes used to evaluate the properties and integrity of a material, component, or system without causing any damage to it. This type of testing is crucial for ensuring safety, reliability, and quality in various industries. NDT is sometimes also referred to as Non-Destructive Evaluation (NDE), Non-Destructive Inspection (NDI), or Non-Destructive Assessment (NDA). By using these methods, industries can ensure that products and structures meet stringent safety standards without compromising their usability or longevity.
Importance of NDT
NDT plays a vital role in industries such as aerospace, oil and gas, automotive, nuclear power, and construction, where the failure of a single component could have catastrophic consequences. By identifying potential issues before they lead to failure, NDT helps in maintaining safety and reducing the risk of accidents.
Quality Assurance: NDT methods are integral to quality control procedures. They allow for the detection of flaws or defects that could affect the performance of materials or components, ensuring that only the best products reach the market.
Safety: NDT ensures that components or structures are safe to use by detecting defects that could lead to failure. This is particularly important in industries where even a minor flaw could lead to significant hazards, such as in aviation or nuclear power plants.
Cost-Effective: By detecting problems early, NDT can help prevent costly repairs or replacements. It also helps avoid project delays by ensuring that all components meet the necessary standards before they are used.
Failure Prevention: Regular NDT inspections can identify issues that might not be visible to the naked eye, such as internal cracks or corrosion. By addressing these issues before they lead to failure, NDT helps prevent accidents and ensures the longevity of components and structures.


Need help?
Get a FREE Career Consultation from our Experts!
NDT Methods
There are several NDT methods, each with its unique advantages and applications. The choice of method depends on the type of material being tested, the type of defects being looked for, and the specific requirements of the industry.
Radiographic Testing (RT):
-
- Description: Radiographic Testing uses X-rays or gamma rays to create images of the internal structure of a material. This method is similar to medical X-rays.
- Applications: Commonly used in the inspection of welds, pipelines, and structural components.
Liquid Penetrant Testing (LPT):
-
- Description: In this method, a liquid penetrant is applied to the surface of the material. After a set amount of time, the excess liquid is removed, and a developer is applied. The developer draws out the penetrant from any cracks or defects, making them visible under ultraviolet light.
- Applications: Widely used for detecting surface-breaking defects in non-porous materials like metals and plastics.
Magnetic Particle Testing (MPT):
-
- Description: Magnetic Particle Testing involves magnetizing a material and then applying ferrous particles to the surface. These particles gather at areas where there is a disruption in the magnetic field, indicating a defect.
- Applications: This method is used primarily for detecting surface and near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials.
Visual Testing (VT):
-
- Description: The simplest form of NDT, Visual Testing involves a visual inspection of a material or component. Advanced VT might include the use of borescopes or magnifying lenses.
- Applications: Used across various industries for initial inspections or as part of a more comprehensive testing protocol.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT):
-
- Description: Ultrasonic Testing uses high-frequency sound waves that are transmitted into a material. The reflection of these waves from internal flaws or the opposite side of the material is used to detect defects.
- Applications: Ideal for detecting internal defects in metals, composites, and other materials.
Eddy Current Testing:
-
- Description: Eddy Current Testing is an electromagnetic method used to detect surface and near-surface defects. It measures the changes in the flow of eddy currents, which are induced in the material by a coil carrying an alternating current.
- Applications: Commonly used in the aerospace and automotive industries, especially for detecting cracks in conductive materials.
Radiographic Film Interpretation (RTFI):
-
- Description: This is a specialized technique where trained personnel analyze radiographs (X-ray or gamma ray images) to identify defects within a material or weld.
- Applications: Essential for ensuring the integrity of welds and castings, particularly in critical applications like pipelines and pressure vessels.
Advantages of NDT
Safety:
NDT methods do not damage the material being tested, ensuring that components remain fit for use. This is especially important in industries like aerospace, where the integrity of every component is critical.
Quality Assurance:
NDT provides reliable, accurate, and consistent results, ensuring that only high-quality materials and components are used in production.
Failure Prevention:
By identifying defects before they lead to failure, NDT helps prevent costly accidents and project delays.
Cost-Effective:
NDT is a cost-effective way to ensure safety and quality. It allows for the early detection of defects, reducing the need for expensive repairs or replacements.
NDT Careers
The field of NDT offers numerous career opportunities across various industries. As infrastructure projects grow and safety standards become more stringent, the demand for skilled NDT technicians continues to rise.
Key Roles in NDT:
- NDT Technicians: Perform tests using various NDT methods to detect defects in materials and components.
- Quality Assurance Specialists: Ensure that products meet quality standards and regulatory requirements.
- Inspectors: Review and interpret test results, making recommendations for repairs or replacements as needed.
Skills and Qualifications Required:
- Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills: Ability to interpret test results and identify defects.
- Attention to Detail: Essential for detecting small defects that could lead to failure.
- Technical Knowledge: Understanding of various NDT methods and their applications.
- Communication Skills: Ability to prepare detailed reports and communicate findings to engineers and other stakeholders.
Conclusion
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) is a critical process in ensuring the safety, reliability, and quality of materials and components used in various industries. By using NDT methods, companies can prevent failures, reduce costs, and ensure that their products meet the highest standards of quality and safety. Whether you are looking to pursue a career in NDT or simply want to understand its importance, this field offers a wealth of opportunities and benefits for both individuals and industries alike.
Need help?
Get a FREE Career Consultation from our Experts!

Explore Our Other Informative Posts

CAREER ADVANTAGE OF LOGISTICS & SUPPLAY CHAIN MANAGMENT
- 2 min read

Hospital Administration: Importance and Job Opportunities
- 2 min read

OIL HUNT STARTS IN KERALA
- 2 min read

Oil And Gas Engineering: Possibilities And Opportunities
- 3 min read

Become a Hospital Administrator: The Steps
- 5 min read

Build an MEP with BIM Career in Just 6 Months
- 4 min read

WHY CHOOSE HOSPITAL ADMINISTRATION?
- 2 min read

Skills You Should Learn to Start a Career in Logistics
- 3 min read

Vizhinjam Port: Powering Kerala’s Logistics & Supply Chain Future
- 3 min read

കേരളാ നിയമസഭാ Reporter TV leadership award സ്വന്തമാക്കി Arrow Wings Academy.
- 1 min read

Logistics vs Supply Chain: What’s the Difference?
- 2 min read

Benefits of a 6-Month Diploma in Virtual Reality (VR) Integrated...
- 2 min read

What Is Hospital Administration?
- 2 min read

VIZHINJAM PORT – NEW OPPORTUNITIES IN THE LOGISTICS SECTOR
- 1 min read

Why is Vizhinjam port Important?
- 1 min read

Why Choose Arrow wings Academy for oil & gas Drilling...
- 2 min read
Salary Scale in oil and gas drilling industry?
- 1 min read

Oil & Gas Drilling – Build a Global Career in...
- 2 min read

FUTURE OF THE OIL & GAS INDUSTRY IN INDIA?
- 4 min read

Is This rig job Risky?
- 3 min read

How to Get a Job on an Oil Rig: A...
- 9 min read

Best Courses in Kerala: A Guide to Quick Job Placement
- 7 min read

Career in Healthcare
- 8 min read

Dominate Oil Rig Training: Dive into the Future with VR”
- 7 min read

Importance of the Oil and Gas Industry
- 7 min read

Logistics and Its Scope in India and Abroad
- 7 min read

A career In Oil and Gas Industry
- 8 min read

What is an oil rig and how does it work?
- 8 min read

What is NDT
- 8 min read

SCOPE OF MEP IN GULF COUNTRIES
- 3 min read

What is MEP Engineering?
- 3 min read

What are Qa and Qc Engineer
- 4 min read

What is Logistics and supply chain management
- 7 min read

IMPORTANCE OF THE OIL AND GAS INDUSTRY
- 4 min read